The simplest organisms living in the Earth's waters, soil and air number up to 15, 000 species. Some of them are the oldest inhabitants of our planet. Over the millions of years since the first living things appeared, most protozoa have remained largely unchanged. But they have learned to adapt well to new living conditions and find ways to survive. One of the most obvious ways of existence of these creatures has been parasiticism, including within the human body.
Parasites
This is a type of complex relationship between two organisms, where one parasite uses another as a habitat or food source.
The organism on which the parasite lives is called the host. It can be permanent as the parasite goes through its entire development cycle in it and intermediately, when the causative organism only lives in it for a certain stage of the life cycle.
Parasitism between protozoa is a type of interaction that not only involves living and parasitizing at other costs, but also endangers the life of the host, as many parasites cause various forms of parasites. serious diseases for humans, livestock and agricultural crops.
The simplest human parasites have selected almost all the organs and systems of the human body, they develop quite actively and sometimes live in them for years. This symbiosis leads to chronic disease and reduced effectiveness of treatment.
Ways to enter the body:
- through hands and mouth;
- through the skin;
- contact;
- transmission from mother to fetus;
- with bites of insects, animals;
Is a general science that studies the phenomenon of parasites, biological characteristics of parasites and distribution areas, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of diseases caused by parasites.
The simplest pathogenic parasites that cause various forms of disease are found almost everywhere. It is fresh and salt water, soil, various household items and household items, public places. A protozoan infection is called a protozoan or protozoan infection.
What are the simplest human parasites
The human body, like the body of any animal large or small, is a very attractive object for parasitic life forms. In addition to protozoa, multicellular parasites (helminths) can reside in the human body.
According to habitat, the simplest species can be endogenous (living inside the human body) or exogenous (having chosen the skin as a habitat). Sometimes, as they grow, the parasites move throughout the body, choosing the most suitable habitat for a particular stage of development.
The microscopic size and the presence of primitive structures allow the simplest parasites to successfully survive and reproduce under the most difficult conditions. All representatives of this species are characterized by a structure consisting of a single cell filled with cytoplasm with intracellular fluid, in which all metabolic processes take place with the participation of organelles(a structure that performs various functions to sustain life)
Migration functions can be performed by flagella, cilia, and pseudo-feathers for this purpose. The main process (food) is carried out in several ways:
- oral swallowing cells;
- flowing around with the pseudopod (pseudopod);
- absorbed by the membrane surface.
Unfavorable conditions can signal the formation of cysts that are resistant to the external environment of the membrane. They are needed so that the simplest human parasites can move from one host to another and can keep a prisoner inside the parasite for several years.
Reproductive cysts are characterized by the formation of a temporary thin shell, which is necessary for a protozoa to briefly divide.
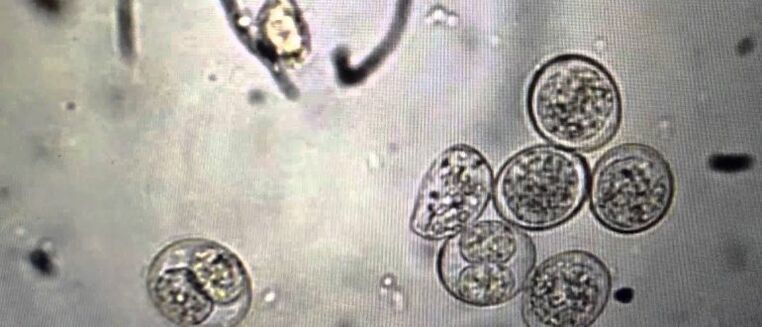
Important!The simplest human parasites are the causative agents of protozoan infections: giardiasis, trichomoniasis, sleeping sickness, amoebic dysentery, malaria.
Types of protozoan parasites
According to the way of reproduction and movement, nutritional nature, there are 4 main classes of the simplest human parasites:
worms
For example, lamblia, leishmania, trichomonas, trypanosomes. They have an elongated oval or pear-shaped body. They may have from 1 to 8 flagellate leaves of thinly developed cytoplasm, including the smallest filaments. They moved forward with a whipworm, as if swirling into the air in front of them. They feed both by absorbing ready-made nutrients and by absorbing them through membranes. Reproduction occurs in most cases by simple division into two daughter cells. The flagellates can live in groups of up to 10, 000 individuals.
Sporozoans
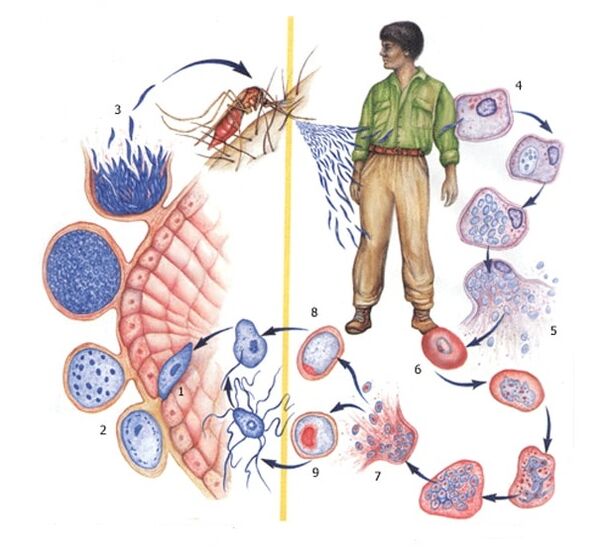
For example, plasmodia malaria, Toxoplasma of Gondia. For representatives of this protozoa, a very complex path of development is characteristic: from the carrier into the human blood, and then into the liver, where the parasite multiplies and affects cells. erythrocytes. Reproductive toxins that cause disease in human hosts. For the next development cycle, the pathogen must again enter the host body, where the maturation of male and female cells and sporulation takes place. After maturation, the spores are destroyed, and the parasite re-enters the host's body. The cycle repeats itself.
Branch
For example, balantidia. For species with cilia, movement with the help of cilia is characteristic. There are two nuclei in the cells of the body: the large nucleus controls all important processes, and the small nucleus plays a major role in the genital side of the existence of protozoa. Reproduction occurs by cell division, for most representatives of the species this happens daily, several times a day. Food is brought into a special cavity (cell mouth) by the movement of cilia, inside the cell, it is processed by the digestive vacuole, and the undigested residues are taken out. .
Sarcode
For example, amoeba is dysentery. It has no fixed shape, forming many prosthetic legs, with the help of which they move and get food. It multiplies by simple division. It can exist in several forms: tissue, luminal, pre-cystic. The type of tissue that lives only in the patient's intestines. The rest of the forms can also be found in the host's body.
Important!The primitive structure, the formation of cysts, the simplest mode of reproduction, the microscopic size, all these factors allow the simplest parasites to penetrate the most protected tissues of the body. body and, in the absence of side effects, they become the source of a number of serious and sometimes difficult to diagnose medical conditions.
What diseases are caused by protozoa?

The parasitic way of life of the simplest microorganisms, in addition to the above factors, is facilitated by their ability to breathe anaerobically, although many species can utilize dissolved oxygen.
Diseases caused by protozoan parasites include:
Malaria
The main symptoms are fever, joint pain, vomiting, anemia, convulsions. There may be an enlarged spleen. Malaria is characterized by a relapse of the disease, with periods of rest and exacerbations. Depending on the type of pathogen, forms are distinguished: three-day, four-day and tropical. The disease is common in Africa and South Asia. For centuries, as today, the main remedy for treatment was quinine, a medicine made from the bark of the cinchona tree. Despite the creation of synthetic analogues, deaths from infections still occur in areas that do not receive modern medical care.
Amoeba (amoeba dysentery)
The disease is caused by the simplest parasitic amoeba of the ironic class of dysentery. Infection can be intestinal and gastrointestinal (developing in the liver). 7-10 days after infection, the first symptoms appear: abdominal pain, weakness, low fever (up to + 37, 5 ° C). About 10% may have severe diarrhea, accompanied by blood and mucus. Every third infected person develops a fever. It is characterized by an enlarged liver and in some cases a liver abscess. If not treated promptly, prolonged diarrhea makes the patient's body dehydrated, weak and exhausted. Outbreaks of the disease are specific to countries with hot climates.
Giardiasis
This disease is caused by the simplest of the class lamblia. These parasites have four pairs of flagella and a sucking disc, which they attach to the inside of the small intestine. When infected, symptoms appear: pain and bloating in the upper abdomen, rumbling and nausea, disruption of the normal functioning of the intestines, damage to the skin (atopic dermatitis), abnormalities in the functioning of the intestines. gallbladder, general weakness and loss of strength, poor appetite and sleep. Giardiasis is common in hot climates in Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
Leishmaniasis
The disease is caused by a parasite leishmania of the flagellate class. The main symptom of cutaneous and mucosal leishmaniasis is skin lesions in the form of ulcers. With the mucocutaneous form, edema and deformity may occur. If it involves the respiratory tract, in rare cases it can be fatal. Organs are characterized by enlarged liver and spleen, fever and anemia. The disease is common in 88 countries, mainly countries with tropical and subtropical climates.
Trichomonas
The disease is caused by the parasite Trichomonas belonging to the flagellate class. The genitourinary system is affected. The main symptoms in women are itching and burning, congestion of the external genitalia, discharge with an unpleasant odor, and sometimes discomfort during sex and urination. In men, in most cases, the disease is asymptomatic, sometimes painful with urination and discharge, symptoms of prostatitis may appear.
Balantidiasis
The causative agent of the disease is a parasite of the class ciliates balantidia. A characteristic symptom is abdominal pain, diarrhea, and mucous membranes of the tongue. In the acute case of the disease, there may be an increase in temperature, signs of general intoxication. Infection can also be chronic, with intermittent periods of remission and exacerbations. In complicated cases, intestinal perforation and peritonitis can occur.
Toxoplasmosis
The disease is caused by the parasite Toxoplasma Gondia, a spirochete parasite. Characteristic symptoms of the disease are damage to the eyes, nervous system, heart muscle, swollen lymph nodes, liver, and spleen. It progresses mainly in the chronic form. Usually, the primary infection is easy, under the guise of a common ARVI. After that, immunity appears permanent, and no further infection is possible. The greatest danger to the fetus during pregnancy: if the child survives, there will be severe damage to the nervous system and eyes.
Sleeping sickness
The disease is caused by the simplest parasite of the flagellate class, the Gambian or Rhodesian trypanosome. The characteristic signs in the early stages are fever, headache, and joint pain. After 7-20 days, the second stage of the disease begins: disturbances in perception of the surrounding world, disturbances in coordination of movements, numbness and sleep disturbances. Outbreaks of the disease are localized in some tropical regions of Africa, inhabited by the main vector of the tsetse fly;
Chagas disease
The causative agent of the disease is a parasite of the flagellate class Trypanosoma cruzi. The main symptoms are fever, swollen lymph nodes, headache, and swelling at the site of the bite. In the early stages, signs of the disease may be absent, and after 8-12 weeks, additional symptoms may begin to develop in 30-40%: increased heart ventricles, enlarged esophagus, bulginglarge intestine. The second stage of the disease can last 10-30 years after infection. The infection is most widespread in Latin America.
Important!Most of the simplest parasites enter the human body if the basic rules of hygiene and personal hygiene are not observed.
Pathways of infection
The entry of any microorganism into the human body can occur through penetration through the skin or through natural openings. For most protozoan parasites found in the environment, methods of infecting humans are limited to the four most common methods:
- Contact and passport. This route of infection is available to the simplest organisms that violate the rules of hygiene and personal hygiene. After all, most microorganisms, when transferred from one host's body to another, can form cysts and remain in this state until they enter a favorable environment. benefit, or in other words inside a person. Infection can happen at any time: shaking hands, using other people's household items (towels, linens, dishes), washing hands with dirty water (in ponds);
- Fecal-oral (giardia). In this case, the infection occurs when the parasites leave the intestines in stool or vomit. If the rules of hygiene are not followed, the parasites will enter the water, food or hands of the new host and enter the body. Poorly washed vegetables and herbs can also become a source of infection, and for children, dirty hands after playing in the sandbox or with pets;
- Through contaminated food (toxoplasma infection). The meat of most animals, especially wild animals, can contain protozoan parasites that, if not heat-treated enough, will enter the human body. Contamination can also occur through unsanitary dairy products and raw fish without adequate heat treatment;
- Transmission (malaria, sleeping sickness). Infection occurs by transmission of the pathogen through the saliva of a carrier when bitten. The disease is transmitted by infected insects directly to susceptible organisms.
In addition to the main methods of infection, infection can occur in a number of other, much less common ways:
- Transplacental transmission with penetration of protozoa parasites from the infected mother through the placenta to the fetus;
- Hemocontact when blood contaminated with parasites enters the patient's body (during medical procedures, drug injections, during sexual intercourse);
- Sexual transmission occurs only during sexual intercourse.
Prevent
Prevention of infection with protozoa consists, first of all, of observing all the rules of hygiene and hygiene. Elimination of the possibility of a parasitic infection can be achieved by judicious implementation of a number of recommendations:
- Enough heat treatment of meat, dairy and fish products (compliance with the heat regime according to technology). Pay special attention to products that have not undergone hygienic control;
- Thoroughly wash fruits, vegetables, berries and herbs, preferably with boiling water. If heat treatment is not possible, especially for children, it is better to remove the skin;
- Regular physical examination, especially if protozoan infection is suspected;
- Comply with a sexual partner and refuse to use drugs;
- In the prevention of infection caused by insect bites, specific measures can be applied: using drugs, killing mosquitoes, trapping and repelling mosquitoes, killing transgenic (malaria-resistant) mosquitoes, and making vaccines.
Important!Of great importance in preventing any infection, including the simplest human parasites, is the level of resistance of the body. After all, if the cyst is exposed to unfavorable conditions, where it lacks nutrition or the immune cells continuously attack the foreign body, the parasite either dies or leaves the host's body.
There are a number of foods that are natural immune stimulants (garlic, ginger, broccoli, carrots, green tea) which, when consumed in a balanced manner, can be invaluable in assisting the body in theenhance immunity.
In addition, some products have an adverse effect on the growth and reproduction of protozoa, especially those that have settled in the gastrointestinal tract: pearl barley porridge, dried fruit, baked apples, vegetable oil, vegetable stew. When treating parasites, it is necessary to limit or completely exclude products that stimulate fermentation: baked goods and sugar.
Currently, the pharmaceutical industry offers many expensive antiparasitic drugs. However, their effective use can only be achieved in combination with preventive measures and adherence to a certain diet, the composition of which can be advised by a specialist. subject.
Don't forget the folk remedies, proven over many generations and many generations. In the case of a combination of all methods and methods under the supervision of a doctor, parasites will have very little chance.
Conclusion
At the beginning of the 21st century, it can be noted that mankind has achieved a lot in the development of parasitology. The message of a new discovery about a particular drug is always cheerfully received by those who need help and treatment today.
The simplest human parasites are still a serious problem in many countries, where the level of development of medicine and society at large leaves much to be desired. There are many places on our planet where diseases like malaria, sleeping sickness, leishmaniasis and many others are rampant. And people wait and hope that people have a chance to live disease-free.
Parasitic diseases of our time are relevant, they require social interaction in all areas of human life, in order to improve medical care for the population, to comply with the rules and standards. standards of personal and public hygiene, implementation of disease prevention measures and educational and environmental hygiene. of natural reservoirs of pathogenic organisms.
Currently, in many countries of the world, various scientific studies are being carried out in the field of parasitology:
- develop a scientific basis and methods for monitoring infectious and parasitic infections;
- to study the biological characteristics and pathogenic variation of the main diseases caused by protozoan parasites;
- quality control and environmental safety of meat and fish products;
- carry out basic research to study the development of pathogens of parasitic diseases, their genetic variation, ecology.